The 7TBRP develops advanced MRI acquisition techniques to investigate brain structure and function.
Diffusion Imaging
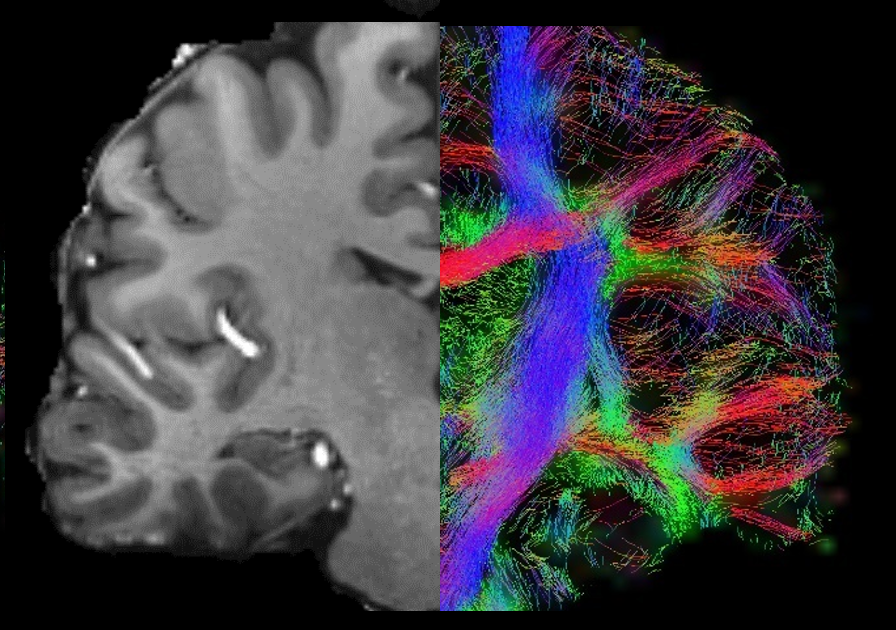
Multi-shell and high-resolution diffusion MRI acquisitions allow for the extraction of advanced metrics and modeling of the tissue microstructure in the brain.
Imaging parameters
- 1.5mm isotropic, b-values up to 3000 s/mm2, 91 directions, TE=78ms, acquisition time=9:40min, suitable for diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI), standard model imaging (SMI), and diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI)
- 1.5mm isotropic, b-values from 0 to 1000 s/mm2, in intervals of 50 s/mm2, 10 directions each shell, suitable for intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM)
- 1mm isotropic, b-values up to 1000 s/mm2, suitable for non-human primates
Susceptibility Weighted Imaging and Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping
High-resolution and 7T tailored methods allow for the characterization of the cerebral microbleeds and iron deposition in the brain.
Imaging parameters
- 0.55 mm isotropic, 3D monopolar GRE, multi-echo TEs from 5 to 20 ms, suitable for quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM), T2* mapping, and microbleed detection
- 0.2×0.2×1.0 mm3, 2D GRE, multi-echo TEs from 15 to 30 ms, suitable for lesion rims detection, QSM, and T2* mapping.
Cerebrospinal Fluid Imaging
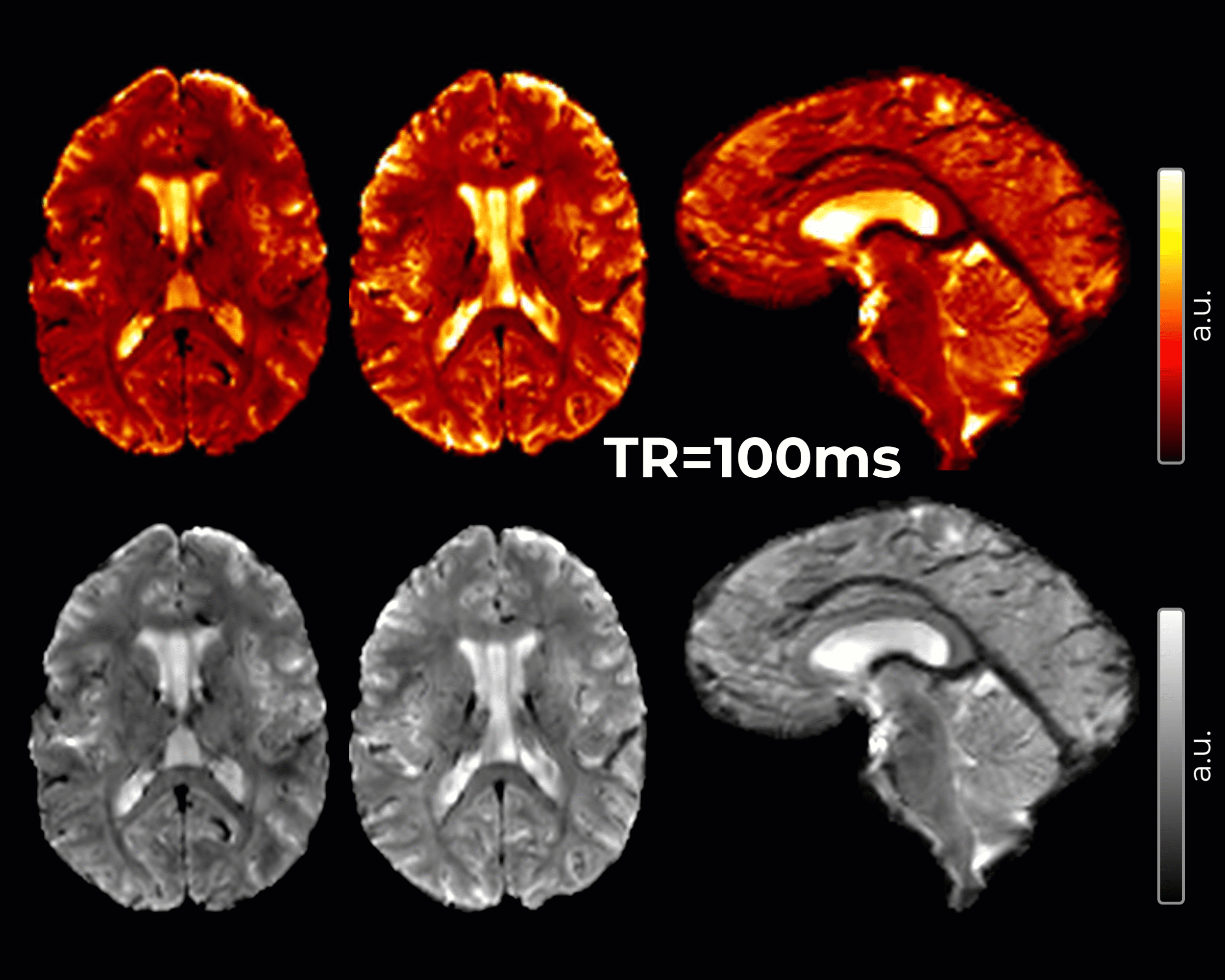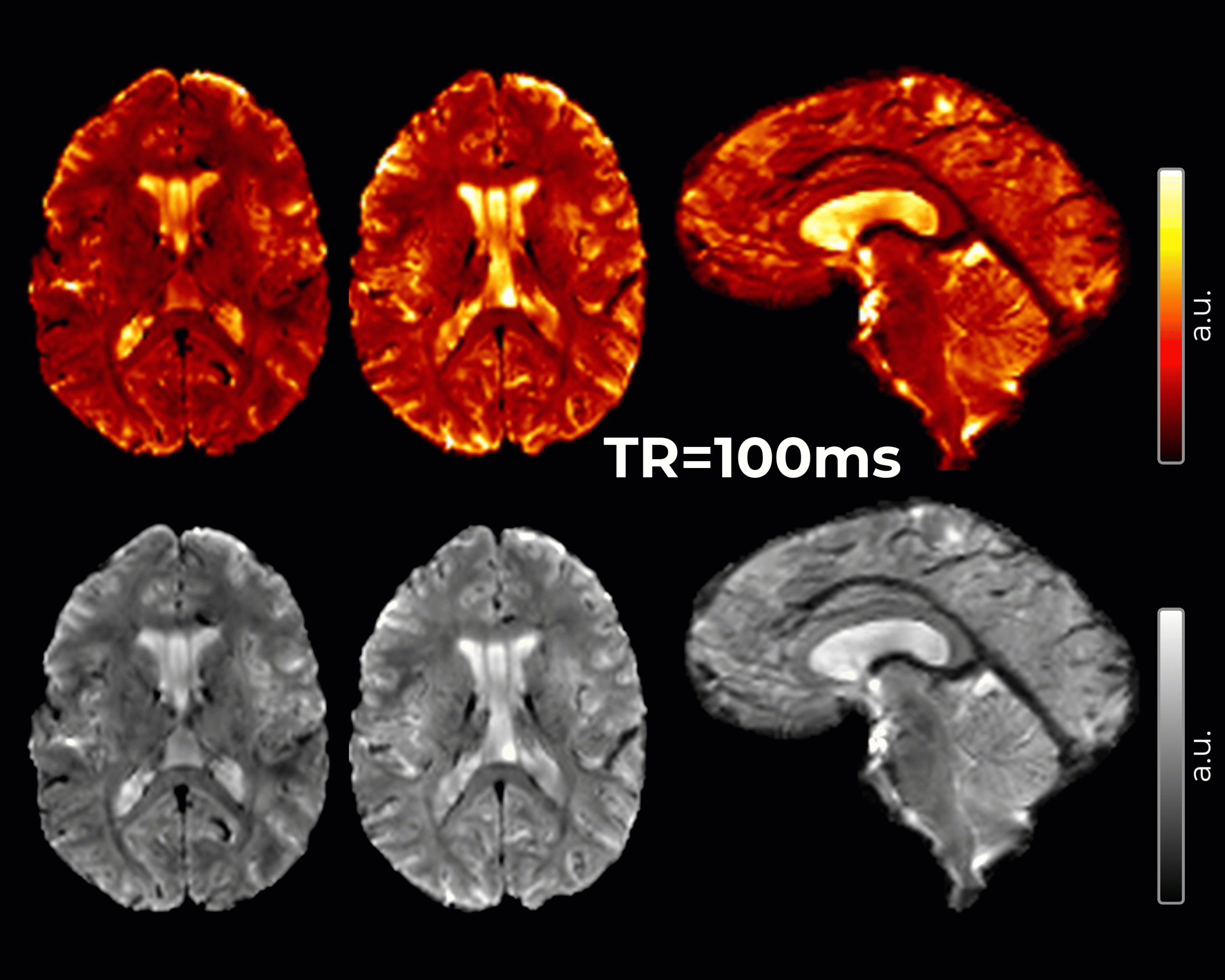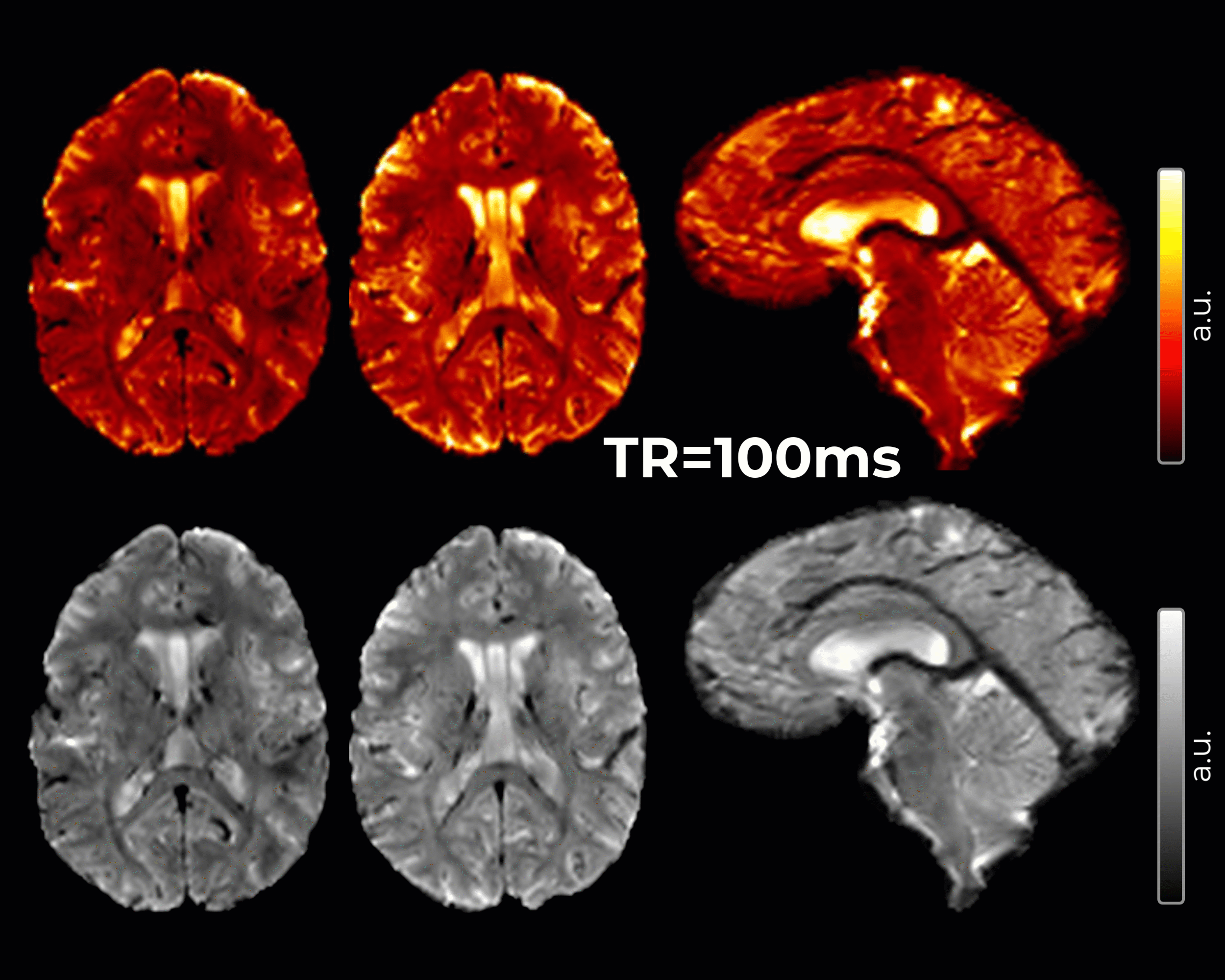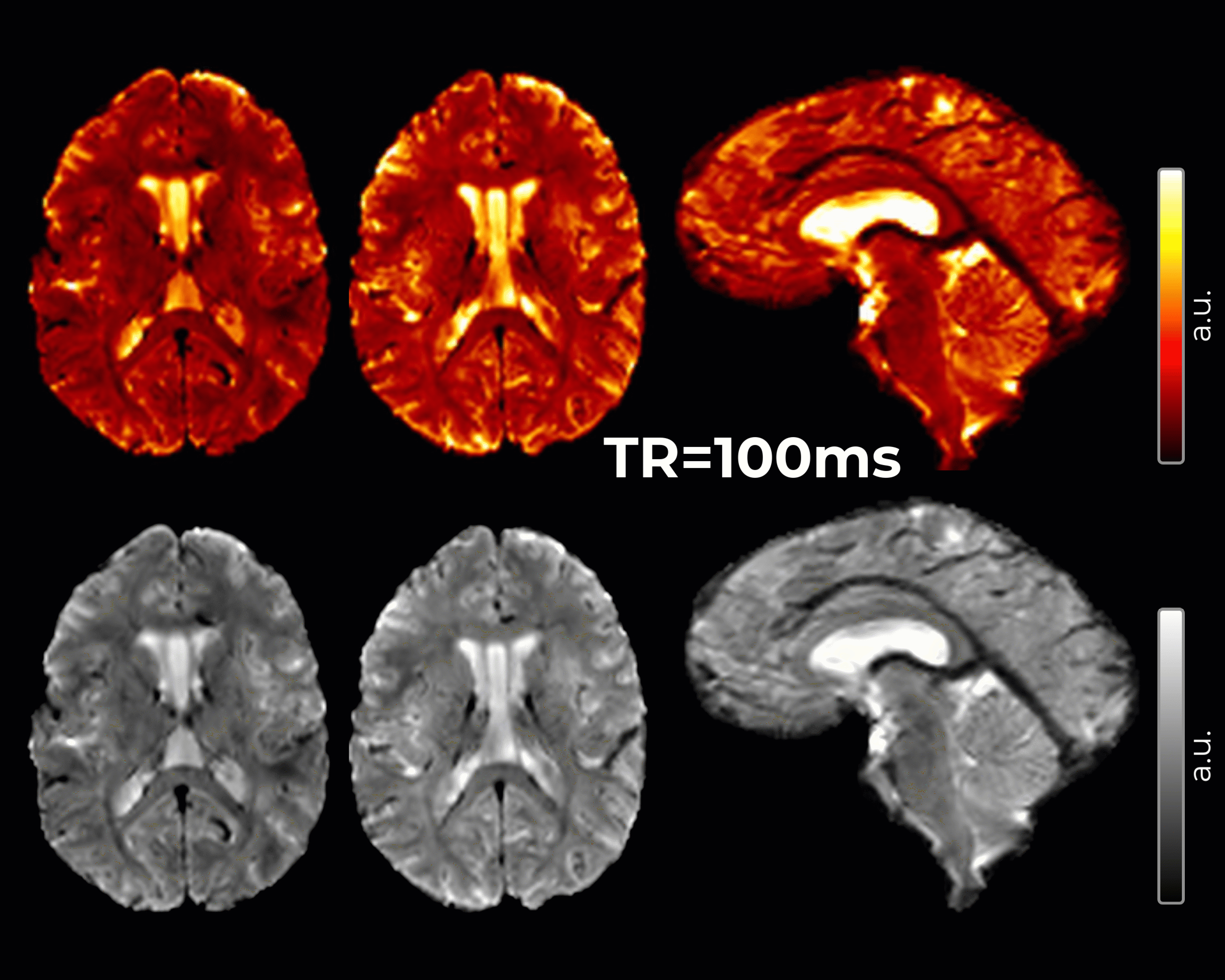 An innovative method for Imaging of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pulsatility has been developed to inform the brain fluid dynamics involved in the clearance of cerebral metabolic waste and to characterize the frequency and spatial localization of whole-brain CSF pulsations.
An innovative method for Imaging of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pulsatility has been developed to inform the brain fluid dynamics involved in the clearance of cerebral metabolic waste and to characterize the frequency and spatial localization of whole-brain CSF pulsations.
Imaging parameters
- 2 mm isotropic resolution, TE=20ms, TR=51ms, acquisition time varies by slice vs. slab coverage
Publications
- Martins T, de Almeida B, Wu M, Wilckens KA, Minhas D, Ibinson JW, Aizenstein HJ, Santini T, Ibrahim TS. Characterization of pulsations in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid using ultra-high field magnetic resonance imaging. Front Neurosci. 2024 May 9;18:1305939. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1305939. PMID: 38784099; PMCID: PMC11112101.
High-Resolution Echo Planar Imaging

The combination of high-resolution echo planar imaging (EPI) and vascular space occupancy (VASO) allows for functional brain mapping and studying cerebral blood volume changes. When a brain region becomes active, there is a decrease in the blood volume and, therefore, a decrease in the VASO signal.
Imaging parameters
- 2 mm isotropic resolution, 60 slices, TE=20ms, TR=1000ms, acquisition time varies based on number of measurements
- 1.5 mm isotropic resolution, 60 slices, TE=20ms, TR=1000ms, acquisition time varies based on number of measurements
- 1.25 mm isotropic resolution, 60 slices, TE=20ms, TR=1000ms, acquisition time varies based on number of measurements
- 0.8 mm isotropic resolution, 60 slices, TE=20ms, TR=1000ms, acquisition time varies based on number of measurements
Arterial Spin Labeling
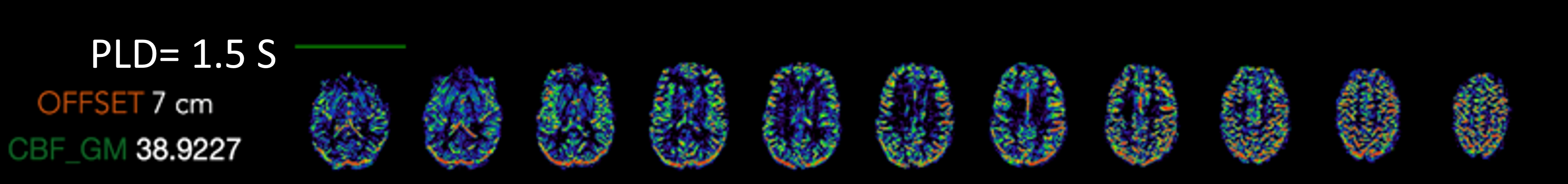
Pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling (pCASL) allows us to visualize the brain perfusion.
Imaging parameters
- 2x2x3 mm3 resolution, TE=19ms, TR=5060ms, varying post labeling delays (PLD) acquisition time = 3.5min
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 1H and 31P

Hydrogen (1H) and phosphorus (31P) magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) allows measurements of the chemical composition and metabolic activity in the brain. The 7TBRP can perform both single voxel spectroscopy (SVS) or 2D & 3D multi-voxel spectroscopy for both 1H and 31P.
Aquisition Types:
- Chemical Shift Imaging (CSI)
- STEAM
- sLASER
- Concentric Ring Trajectory (CRT)
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
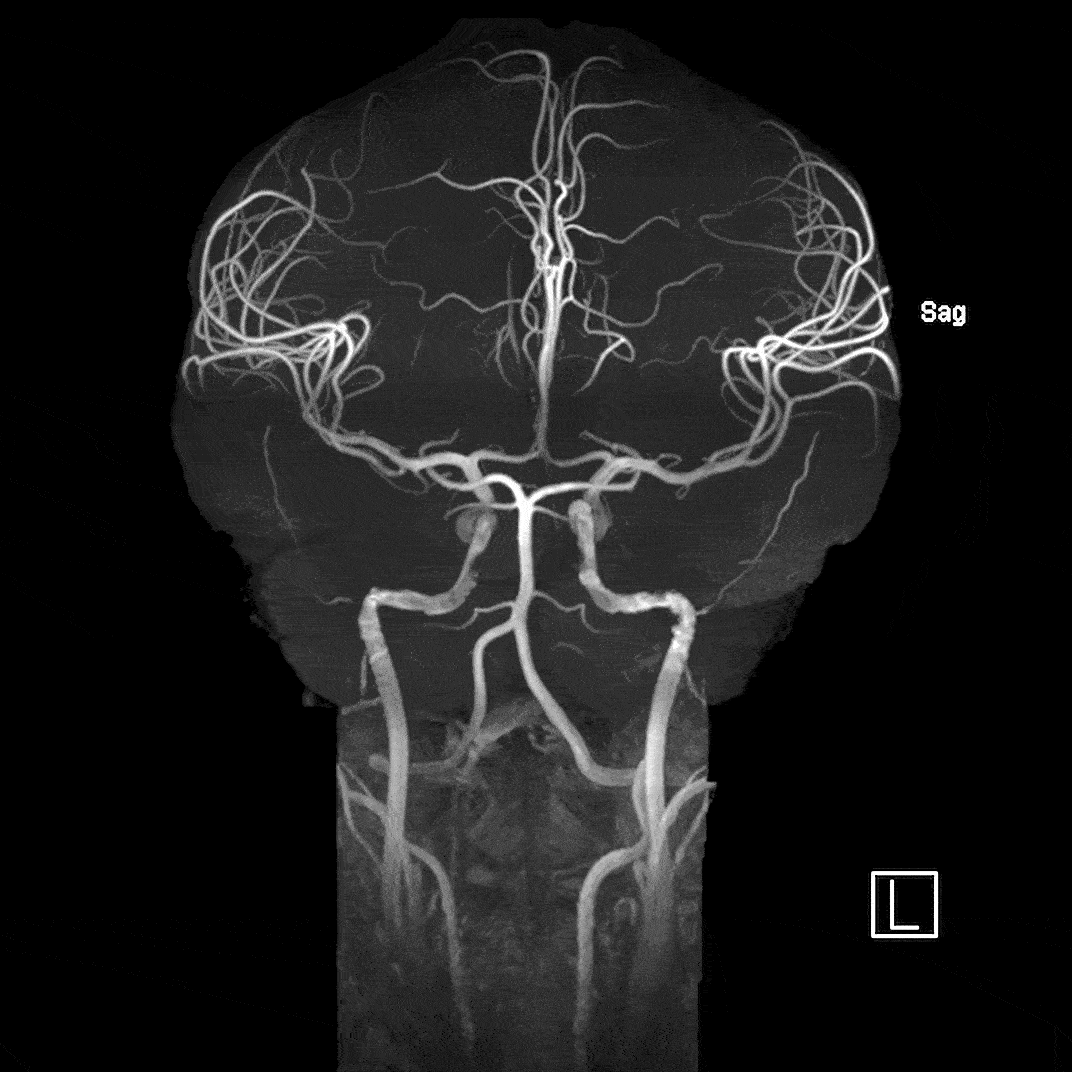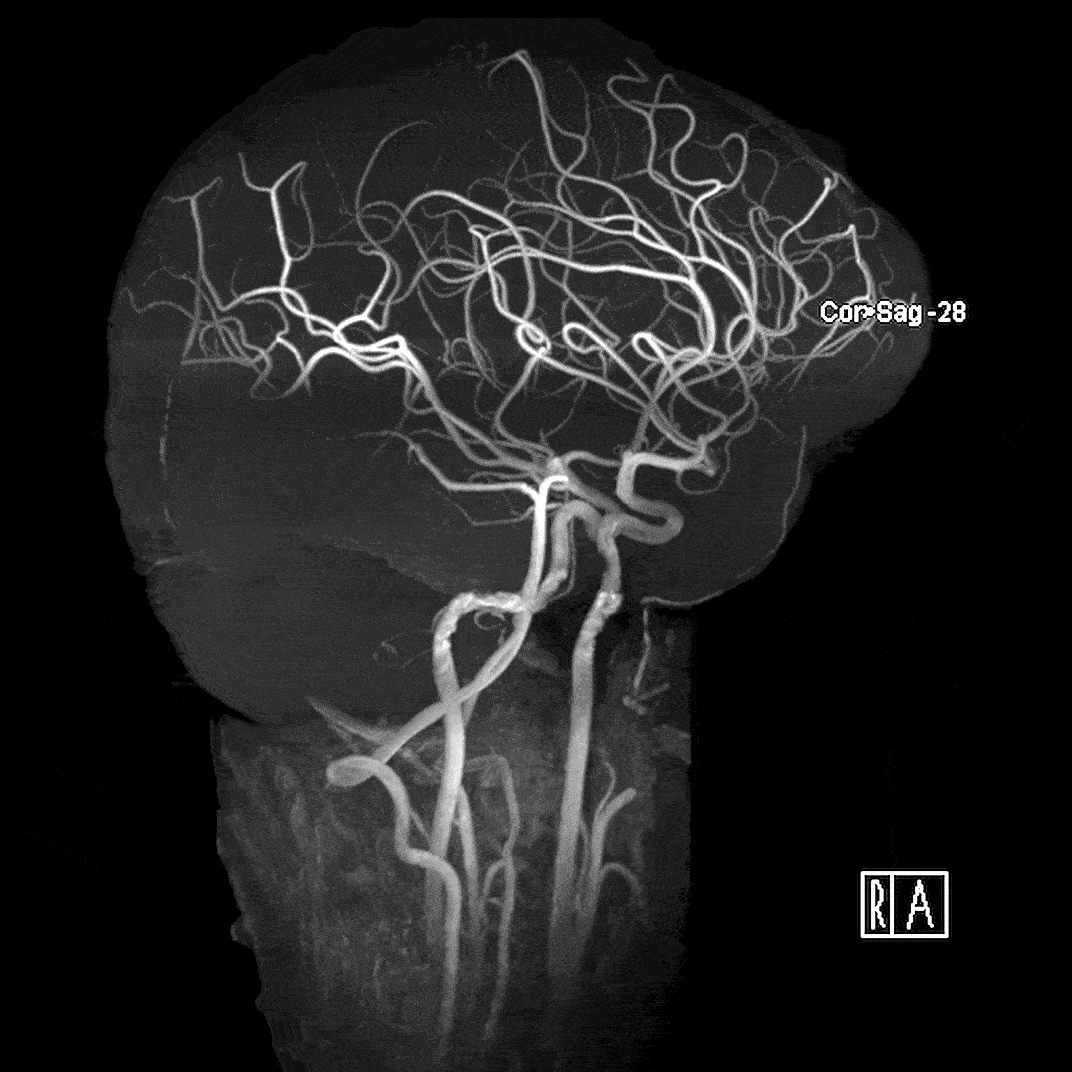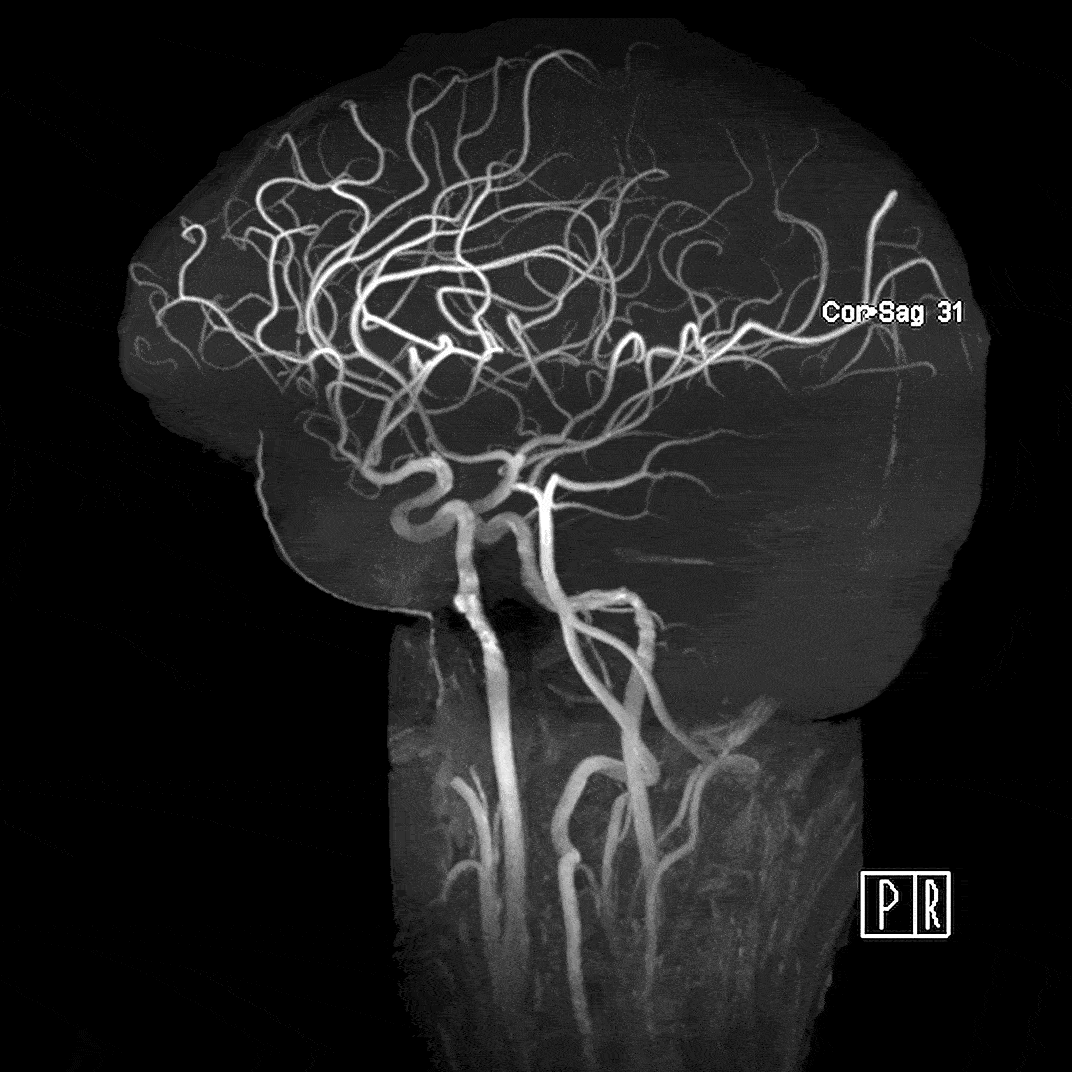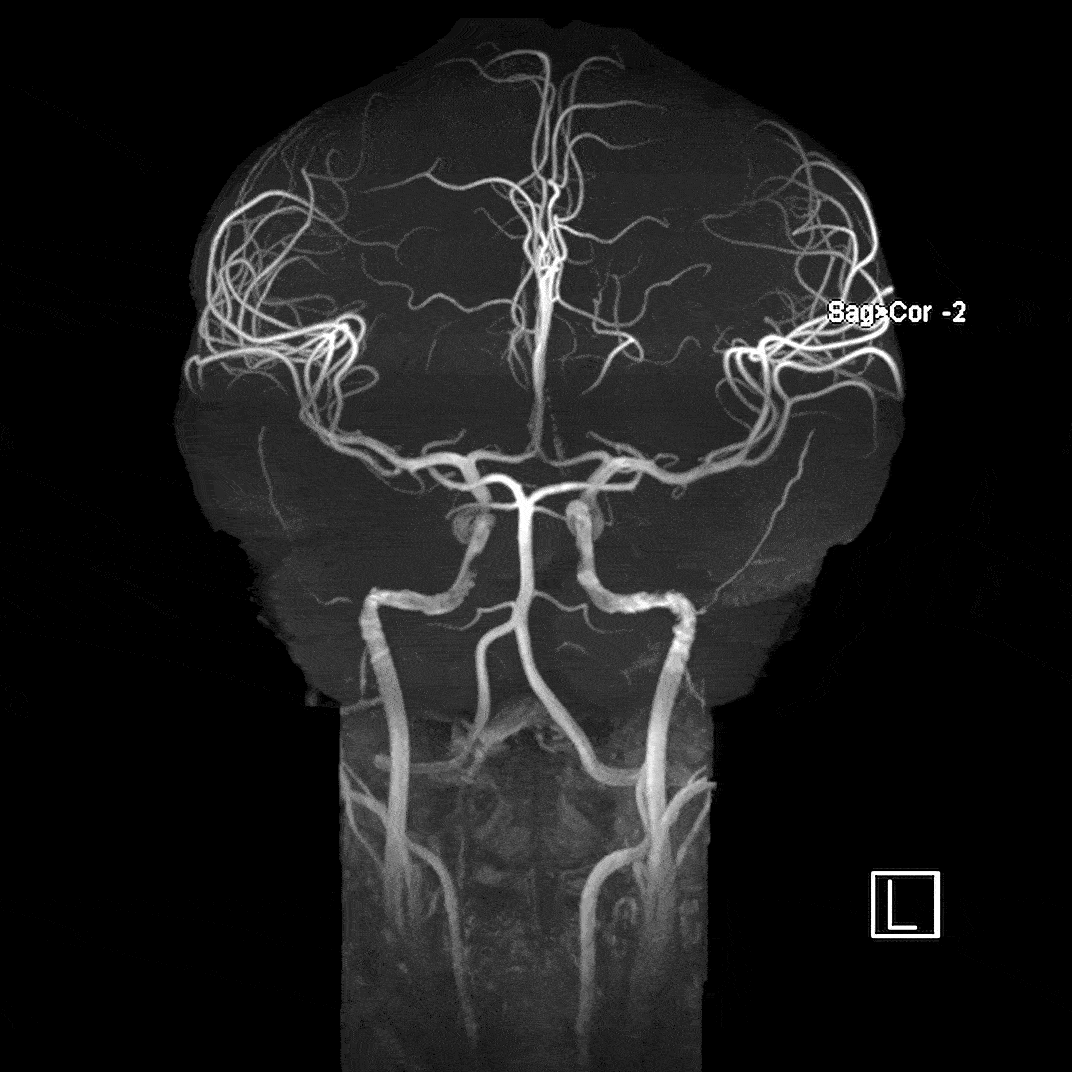
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) highlights flowing blood to detect issues such as aneurysms, narrowed arteries, blood clots, and other blockages. We use Time of Flight imaging to derive the contrast needed to properly visualize the arterioles.
Imaging parameters
- 0.38 mm isotropic resolution, TE=4.5ms, TR=14ms, acquisition time = 11:37 min
High-Resolution Structural Imaging
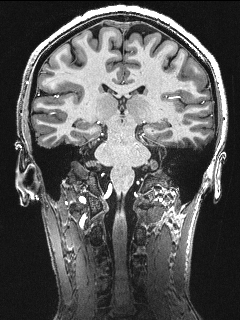
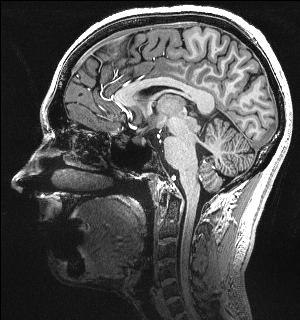
In addition to the modalities above, we also acquire high-resolution T1 and T2w modalities including MPRAGE, MP2RAGE, SPACE, TSE, FLAIR and MT images for brain morphometrics, hippocampal subfields, and locus coeruleus/circle of willis imaging.
Imaging parameters
- MPRAGE: 0.75 mm isotropic resolution, acquisition time = 6 min
- MP2RAGE: 0.55 mm isotropic resolution, acquisition time = 13 min
- SPACE: 0.6 mm isotropic resolution, acquisition time = 10 min
- TSE: 0.375x0.375x1.5 mm3 resolution, acquisition time = 4 min for hippocampus segmentation, 8 min for whole brain
- FLAIR: 0.75x0.75x1.5 mm3 resolution, acquisition time =11.5 min
- MT: 0.4×0.4×0.5 mm3 resolution, acquisition time = 4:38 min
Publications
- Chu C, Santini T, Liou JJ, Cohen AD, Maki PM, Marsland AL, Thurston RC, Gianaros PJ, Ibrahim TS. Brain Morphometrics Correlations With Age Among 350 Participants Imaged With Both 3T and 7T MRI: 7T Improves Statistical Power and Reduces Required Sample Size. Hum Brain Mapp. 2025 Mar;46(4):e70195. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70195. PMID: 40083197; PMCID: PMC11907059.
- Santini T, Koo M, Farhat N, Campos VP, Alkhateeb S, Vieira MAC, Butters MA, Rosano C, Aizenstein HJ, Mettenburg J, Novelli EM, Ibrahim TS. Analysis of hippocampal subfields in sickle cell disease using ultrahigh field MRI. Neuroimage Clin. 2021;30:102655. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102655. Epub 2021 Apr 3. PMID: 34215139; PMCID: PMC8102634.
